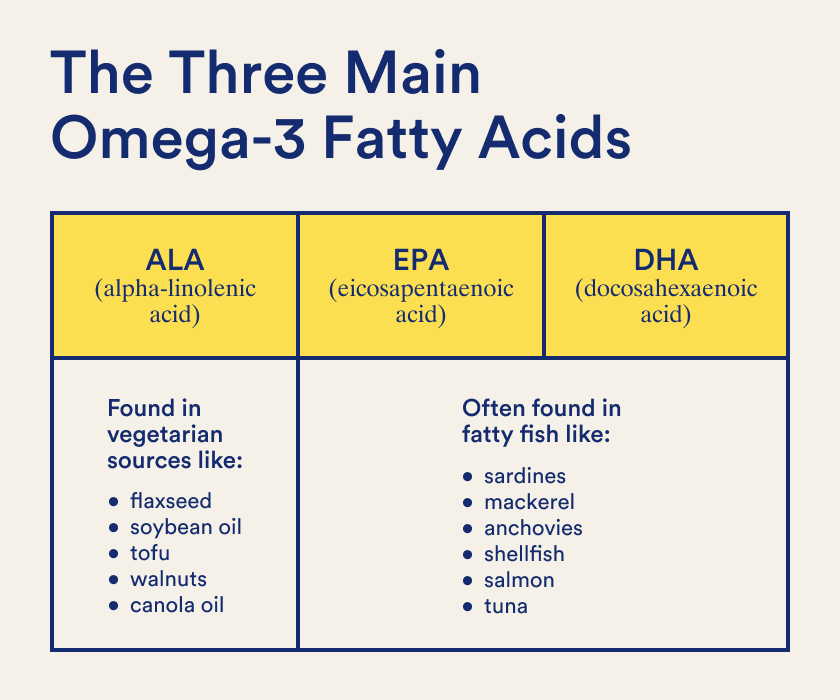
• Your body converts ALA to EPA + DHA. The catch? It can only convert a small amount, less than 15 percent—which explains why many dietary supplement companies promote omega-3 fish oil supplements as a source of omega-3 fatty acids. But since fish actually get their DHA from eating phytoplankton, which get it from eating microalgae, we went straight to the source for our multivitamins—all of which are made with omega-3 DHA from vegan algal oil.* (1)
→ Essential Reading: What’s the Best Multivitamin for Vegans?
Most of us aren’t consuming enough omega-3 DHA
“The amount of omega-3 DHA Americans are getting from their diet is typically below recommended levels,” says Dr. Mastaneh Sharafi, PhD, a dietitian and Ritual’s VP of Scientific Affairs. And that’s to put it mildly. According to national data, 95% of women and men ages 19-50 are not getting their recommended daily intake of key omega-3s (aka DHA+EPA—more on this in a sec). (2-5)
How much omega-3 DHA per day is recommended?
Getting enough omega-3 fatty acids is important—the scientific consensus there is clear. And while there isn’t actually a specific intake recommendation for DHA or EPA established by the Institute of Medicine (IOM), experts and health organizations suggest 250 mg of omega-3s (DHA+EPA) per day. (4, 5)
Why omega-3 supplementation can be a good idea
While we’re all about a food-first philosophy at Ritual—aiming to meet the majority of nutrient needs through food sources, then supplementing to help fill gaps—we also recognize the reality we’re up against, particularly when it comes to maintaining omega-3 levels.*
If you eat plenty of servings of fatty, oily fish on a regular basis, you might be covered. But there are many other barriers of entry—limited access to seafood, dietary restrictions, personal taste preferences, busy schedules—that can make it tricky to meet the recommended intake of omega-3s through diet alone. One simple way to ensure you're fulfilling the body’s omega-3 needs is taking a daily multivitamin formulated with omega-3 DHA.*
→ Essential Reading: Meet Algarithm, Ritual’s Omega-3 Supplier
Look for a clinical-backed formula
Listen: As skeptics, we’ve been in your shoes—the market is saturated, and separating the truly high-quality supplements from the ones that just seem good from the outside is more challenging than ever. One way to separate the wheat from the chaff? Assess each company’s commitment to transparency, and opt for ones that show you the receipts along the way. Third-party quality certification (like USP verification) and clinical testing also point to rigorous standards.
Speaking of clinical testing, Essential for Women Multivitamin 18+ was shown in a university-led clinical trial to increase omega-3 DHA levels by 41% over 12 weeks, significantly greater than placebo. Even better? That gold standard clinical study has been published in Frontiers in Nutrition—a leading, internationally recognized, peer-reviewed journal.*
In other words? It’s a multi backed by one of the highest awards scientific research can achieve.*
→ Essential Reading: Our Clinical Study Is Published—Here’s Why You Should Care
References:
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Fact Sheet For Health Professionals. Retrieved from National Institutes of Health.
- USDA, Agricultural Research Service. Usual Nutrient Intake from Food and Beverages, by Gender and Age, What We Eat in America, NHANES 2013-2016. 2019.
- Zhang Z, Fulgoni VL, Kris-Etherton PM, Mitmesser SH. Dietary intakes of EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids among US childbearing-age and pregnant women: an analysis of NHANES 2001-2014. Nutrients. 2018;10:416.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2015 – 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th Edition. 2015.
- World Health Organization. Interim Summary of Conclusions and Dietary Recommendations on Total Fat & Fatty Acids From the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Fats and Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition. 2008.